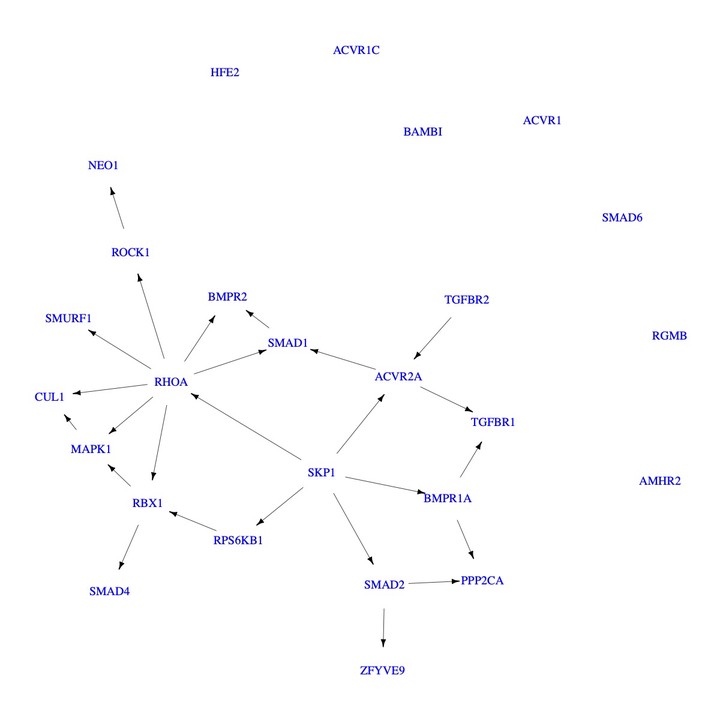
Abstract
Zero-inflated count data arise in a wide range of scientific areas such as social science, biology, and genomics. Very few causal discovery approaches can adequately account for excessive zeros as well as various features of multivariate count data such as overdispersion. In this paper, we propose a new zero-inflated generalized hypergeometric directed acyclic graph (ZiG-DAG) model for inference of causal structure from purely observational zero-inflated count data. The proposed ZiG-DAGs exploit a broad family of generalized hypergeometric probability distributions and are useful for modeling various types of zero-inflated count data with great flexibility. In addition, ZiG-DAGs allow for both linear and nonlinear causal relationships. We prove that the causal structure is identifiable for the proposed ZiG-DAGs via a general proof technique for count data, which is applicable beyond the proposed model for investigating causal identifiability. Score-based algorithms are developed for causal structure learning. Extensive synthetic experiments as well as a real dataset with known ground truth demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method against state-of-the-art alternative methods in discovering causal structure from observational zero-inflated count data. An application of reverse-engineering a gene regulatory network from a single-cell RNA-sequencing dataset illustrates the utility of ZiG-DAGs in practice.